In the ever-evolving landscape of taxation in India, the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) marked a significant shift towards a unified indirect tax regime. GST aimed to simplify and streamline taxation processes, enhance compliance, and promote economic growth. One of the critical aspects of this transformation was the introduction of aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST registration. This article delves into the nuances of Aadhaar-based authentication, the role of physical verification, and their combined impact on the GST ecosystem.
The Advent of Aadhaar in GST
The Aadhaar system, a unique identification project by the Government of India, is designed to provide a distinctive 12-digit identification number to each Indian resident. It has found applications in various sectors, including taxation, where it is used for Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST.
Aadhaar-based authentication under GST was introduced to achieve several objectives:
Enhanced Efficiency:
Aadhaar authentication streamlines the registration process. It allows applicants to verify their identities swiftly, reducing paperwork and administrative hurdles.
Reduced Duplication:
Aadhaar authentication minimizes the chances of duplicate registrations and tax evasion by ensuring that each taxpayer is uniquely identified.
Ease of Compliance:
Once authenticated, taxpayers can easily file returns, claim credits, and conduct other transactions on the GST portal, making compliance more accessible.
Steps for Aadhaar Authentication in GST Registration:
Here are the steps for Aadhar Authentication in GST Registration:
For Primary Authorized Signatory and Promoter/Partner during GST Application:
Step 1: When completing Part-B of the GST application, make sure to select ‘Yes’ for Aadhaar authentication.
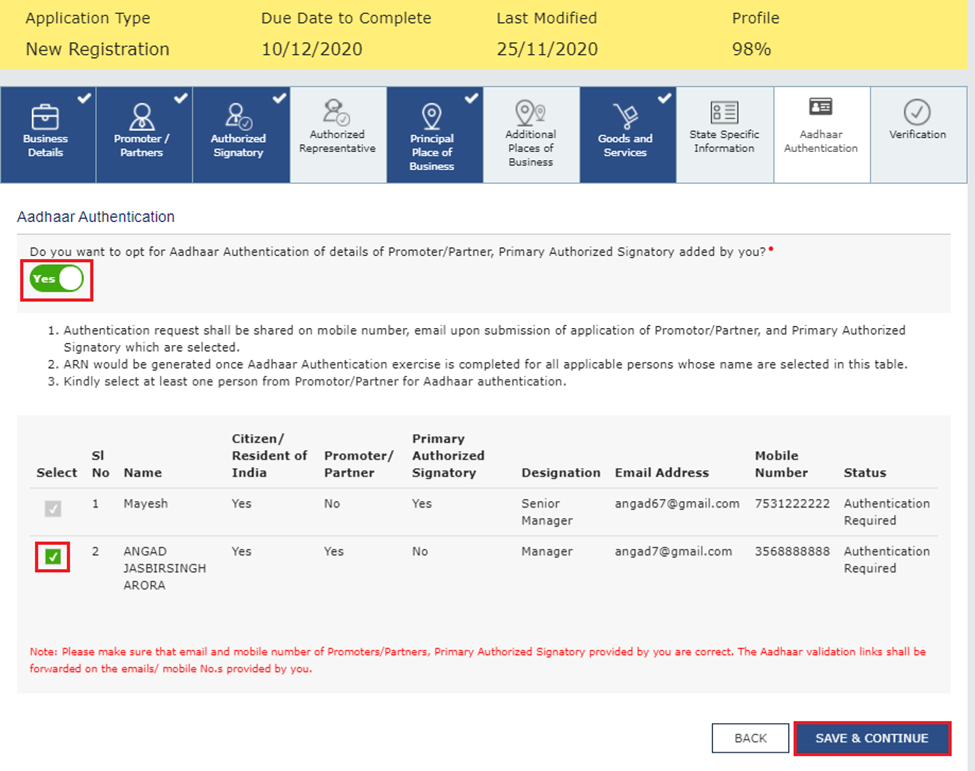

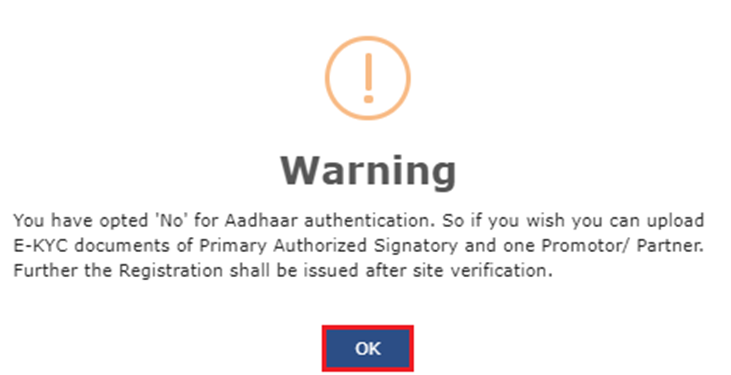
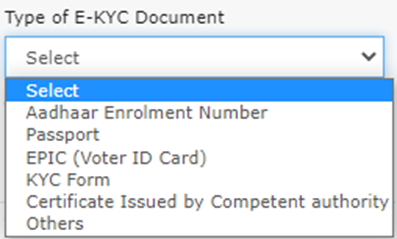
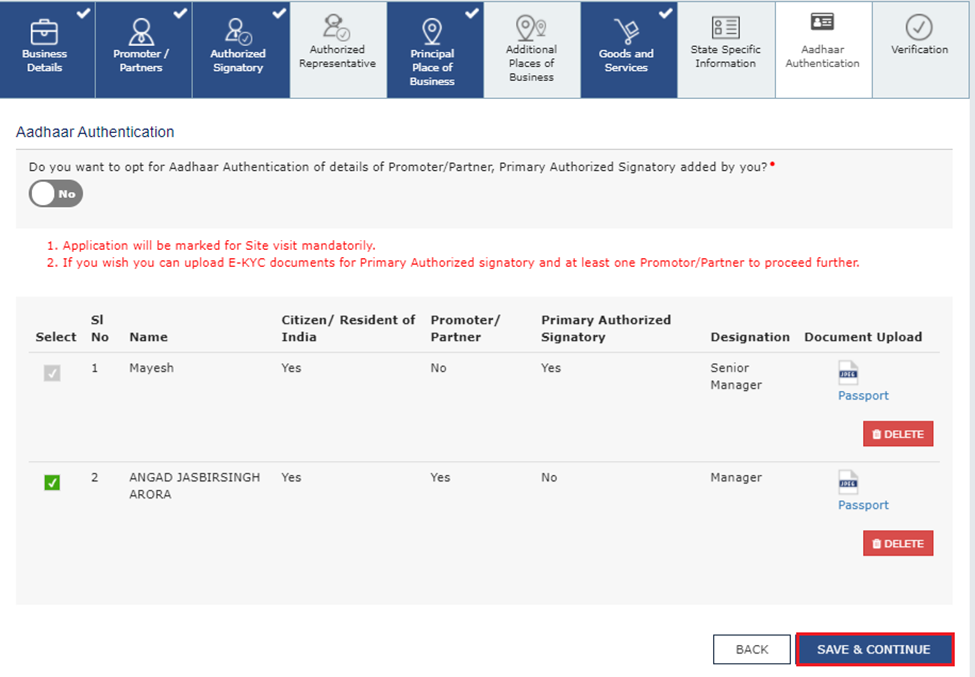
If ‘No’ is chosen, a window will appear (see image below). Click ‘OK’ and proceed to upload e-KYC documents for the signatory and one promoter/partner.



Step 2: An authentication link will be sent to the registered mobile number and email ID mentioned in the application for both the primary authorized signatory and the particular promoter/partner. This link is valid for 15 days.
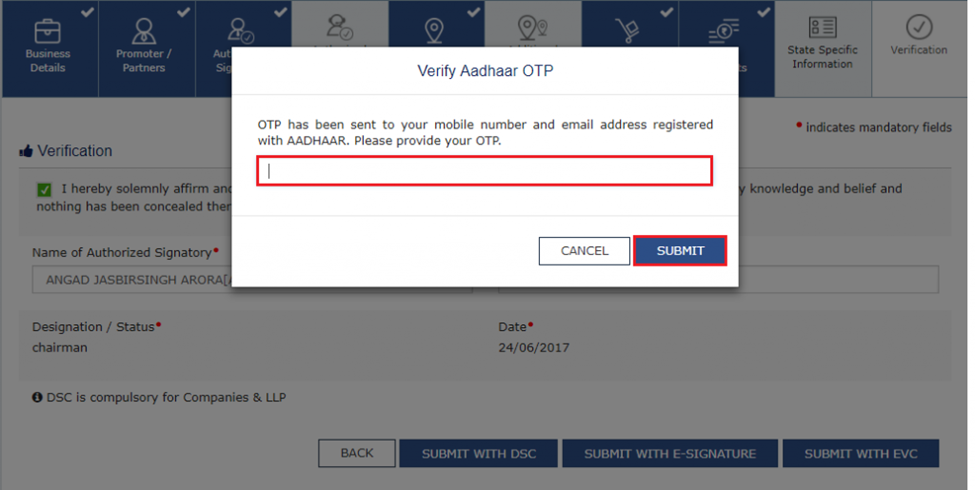

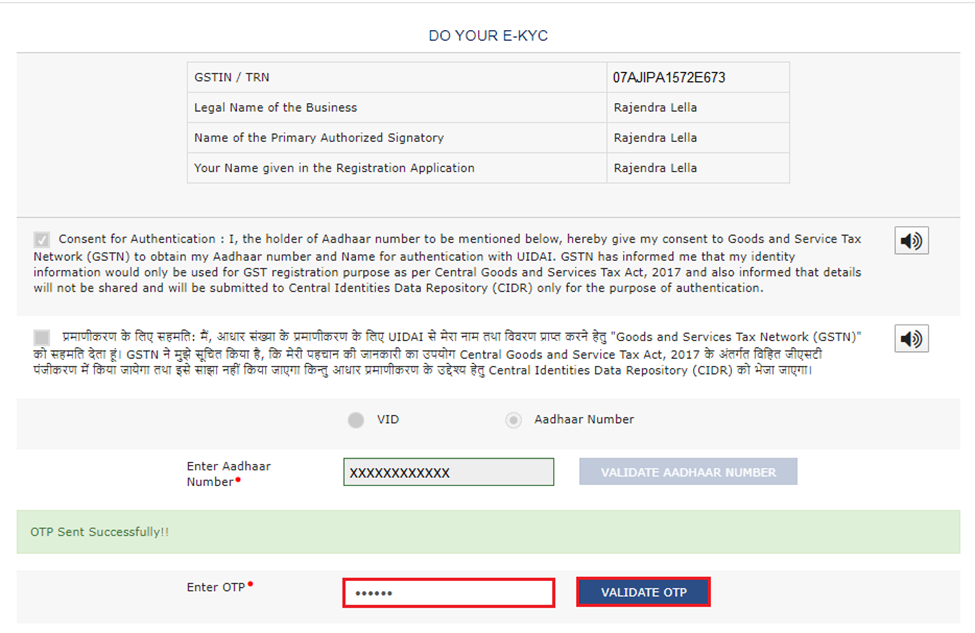
Step 3: Click on the link, and a window will open where you must enter the Aadhaar number and the OTP received on both the mobile number and email. Upon successful authentication, a confirmation message will be displayed. You can request the authentication link again by visiting the GST portal: My Saved Applications > Aadhaar Authentication Status > RESEND VERIFICATION LINK.
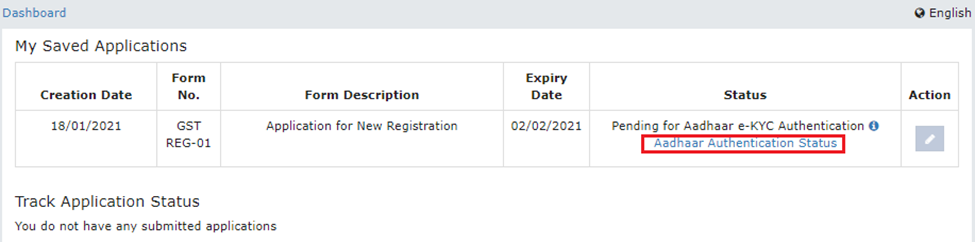

For Existing Taxpayers:
Step 1: Log in to the GST portal and go to the “MY PROFILE” page. Access the “Aadhaar Authentication Status” section, where you’ll find two options
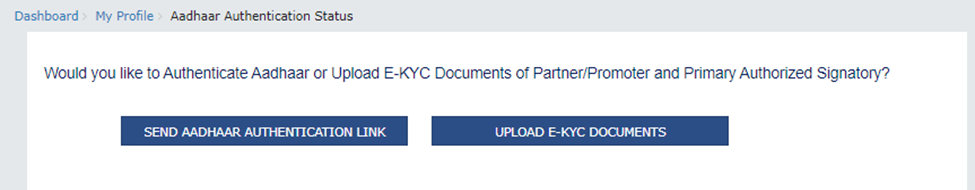

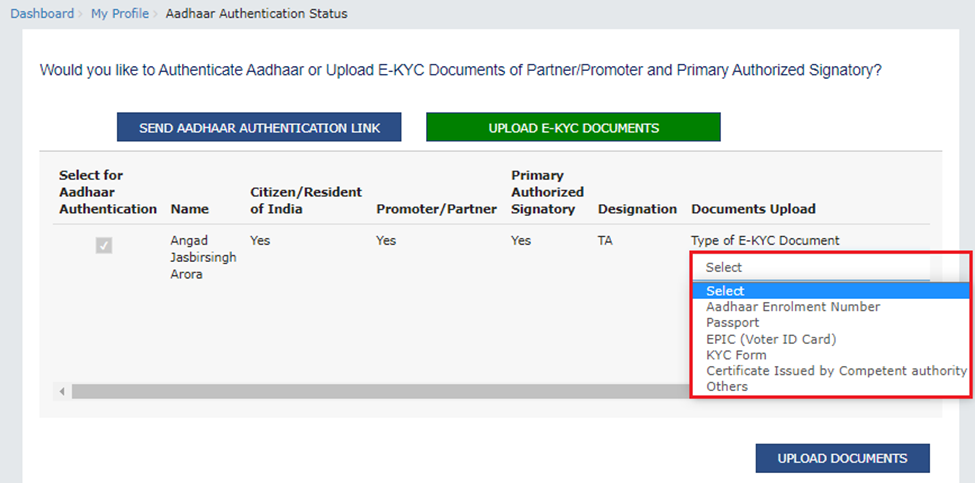
Step 2: Choose between the following two options:
- Send Aadhaar Authentication Link: Check the links received on the email ID and mobile number of the signatory and the particular promoter or partner, and complete the OTP verification.
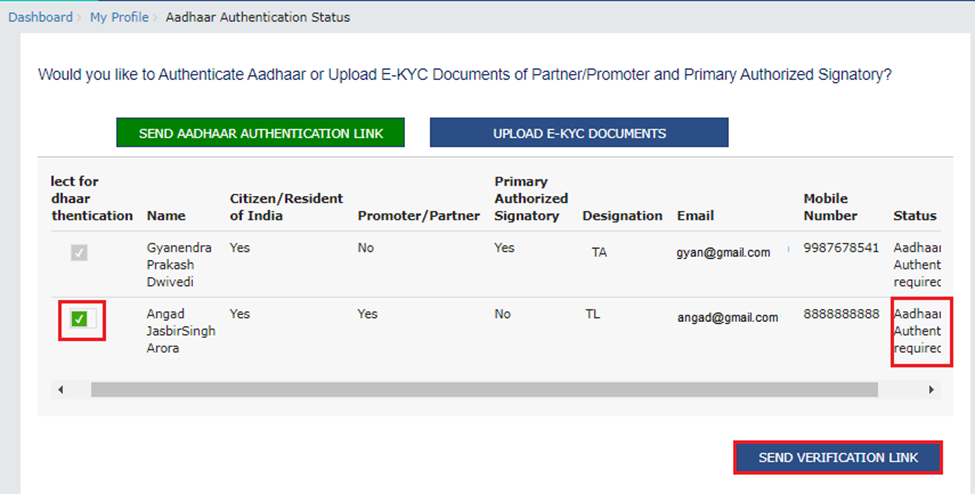


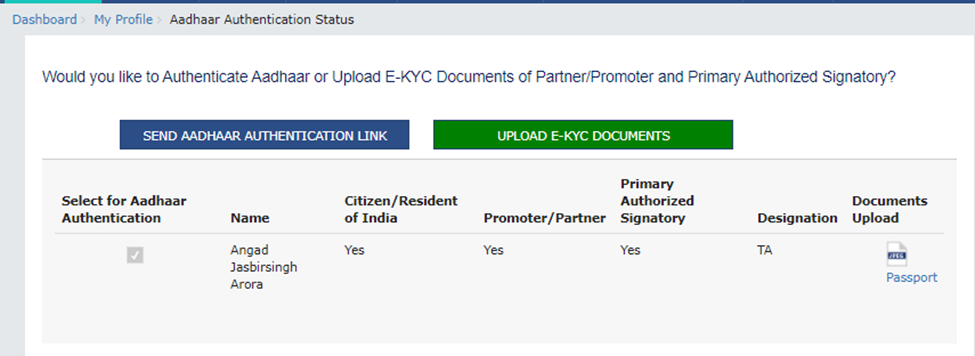
Upload e-KYC Documents: The documents can be approved or rejected by the tax officer. In this case, the taxpayer will be considered e-KYC Authenticated, not Aadhaar Authenticated.


Physical Verification in the Absence of Aadhaar Authentication
While Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST registration streamlines the process for many taxpayers, it’s important to note that not everyone opts for this method. Some applicants may choose not to undergo Aadhaar authentication, or they may encounter issues with the authentication process. In such cases, the GST system resorts to physical verification of the applicant’s principal place of business.
Why Physical Verification is Necessary
Here’s why physical verification is necessary:
Ensuring Authenticity:
Physical verification, as part of Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST, helps confirm that the business location provided by the applicant indeed exists. This is crucial to prevent fraudulent or fictitious registrations, which could lead to tax evasion and other illegal activities.
Validating Compliance:
GST officers utilize physical verification as part of Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST to assess whether the applicant’s business operations adhere to GST laws and regulations. This includes checking if the business maintains proper records, follows invoicing rules, and complies with tax payment requirements.
Preventing Misuse:
By conducting physical verification, as part of Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST, the GST authorities can identify and prevent misuse of the GST registration system, ensuring that only eligible businesses are granted registration.
The Physical Verification Process
The physical verification under the aadhaar-based authentication and physical verification under GST process, in the absence of Aadhaar authentication, involves several steps:
1. Initiating Physical Verification:
- When an applicant chooses not to undergo Aadhaar authentication or faces difficulties in the process, the GST officer initiates physical verification.
- The officer schedules a visit to the applicant’s principal place of business.
2. Notice in Form GST REG-3:
- Within 30 days from the date of the GST registration application, the GST officer issues a notice to the applicant in Form GST REG-3.
- It’s important to note that the date of application submission is determined as the earlier of two dates:
- The date of Aadhaar authentication (if applicable)
- 15 days from the submission of Part B of Form GST REG-01
3. Applicant’s Response:
- The applicant must respond to the notice within seven working days from the date of receipt.
- During this period, the applicant is required to provide the GST officer with all the necessary documents and information to support their application.
4. Verification by GST Officer:
- Following the applicant’s response, the GST officer conducts a thorough verification of the business premises.
- The officer assesses various aspects, including the physical existence of the place of business, its compliance with GST rules, and the accuracy of the information provided in the application.
5. Approval or Rejection:
- If the GST officer is satisfied with the results of the physical verification and believes that the applicant’s business complies with GST regulations, they approve the grant of registration.
- Conversely, if the officer is not convinced of the applicant’s eligibility or compliance, they can reject the application using Form REG-05.
6. Deemed Approval:
- In cases where the GST officer fails to take action within the specified timelines, the registration is deemed to be granted. This is to prevent undue delays and ensure that businesses can operate smoothly.
Cases of Deemed Approval
| Case Description | Timeline |
| Successfully Completed Aadhaar Authentication or Exempted | 3 working days from application submission |
| Opted but Failed to Complete Aadhaar Authentication | 21 working days to send notice in form REG-3 |
| Not Opted for Aadhaar Authentication | 21 working days from application submission |
| Opted but Failed to Complete Aadhaar Authentication, Notice Issued, and Responded in REG-4 | 7 working days from receipt of response, information, or required documents |
Challenges and Considerations
While Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST is a crucial component of the GST registration process, it can pose challenges and considerations for both applicants and GST authorities:
- Time-Consuming: Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST can be a time-consuming process, which may delay the issuance of GST registration. Businesses may face operational disruptions during this period.
- Documentation: Applicants must maintain comprehensive records and ensure their business operations are in compliance with GST laws to pass the Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST process successfully.
- Transparency: The Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST process aims to maintain the integrity of the GST system. However, it’s essential that this process remains transparent and does not lead to harassment or undue delays for genuine businesses.
Mandatory Cases of Aadhaar Authentication
Mandatory Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST is applicable to specific categories of individuals and entities as outlined in Section 25(6C) of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act and further defined in Rule 8 of the CGST Rules, 2017.
Here are the key categories for which Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST is mandatory:
Authorized Signatories of All Types:
Aadhaar authentication is mandatory for individuals serving as authorized signatories for GST registration. This includes individuals who are authorized to act on behalf of a business for GST-related matters.
Managing or Authorized Partners of a Partnership Firm:
In the case of a partnership firm, managing or authorized partners are required to undergo Aadhaar authentication when applying for GST registration. This ensures that individuals with significant roles in the partnership are uniquely identified.
Karta of a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF):
The Karta, who is the head or manager of a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), must undergo Aadhaar authentication when applying for GST registration on behalf of the HUF. This helps in uniquely identifying the Karta responsible for GST compliance.
Biometric-Based Aadhaar Authentication
Here’s a comprehensive overview of biometric-based Aadhaar authentication:
- Security Boost: Utilizes unique biometric data (e.g., fingerprints, iris scans) for robust identity verification.
- Accuracy: Highly precise, minimizing the risk of false identification.
- Versatile Applications: Widely employed in GST registration, financial services, government programs, mobile SIM activations, and access control.
- Privacy and Security: Emphasizes the need for stringent data protection and follows regulatory guidelines to secure biometric information.
- Future Evolution: Expected to advance with emerging technologies, including potential integration of advanced biometric identifiers like facial recognition.
Role of Physical Verification in GST
The role of physical verification in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system is pivotal for ensuring the authenticity and compliance of businesses. Physical verification plays a crucial role in the following aspects:
Authenticity of the Business Premises:
- Physical verification is used to confirm the existence and authenticity of the applicant’s principal place of business.
- GST officers visit the physical location mentioned in the GST registration application to verify its presence and operational status.
Verification of Compliance with GST Regulations:
- During physical verification, GST officers assess whether the business adheres to GST laws and regulations.
- They verify whether the business maintains proper records, follows invoicing rules, and complies with tax payment requirements.
Preventing Fraudulent Registrations:
- Physical verification acts as a safeguard against fraudulent or fictitious registrations. This helps in preventing tax evasion, which can be a significant concern without proper verification.
Maintaining the Integrity of the GST System:
- Physical verification contributes to the overall integrity of the GST system by ensuring that only legitimate businesses receive GST registration.
- It helps in maintaining the credibility of the GST regime and prevents misuse of the registration process.
Addressing Non-Compliance:
- In cases where businesses are found to be non-compliant during physical verification, appropriate actions can be taken to bring them in line with GST regulations.
- This can include issuing notices, penalties, or initiating further investigations.
Timely Granting of Registration:
- While physical verification may add some time to the registration process, it ensures that businesses granted GST registration are genuine and meet the necessary criteria.
- It helps in reducing the chances of fraudulent registrations, which can have adverse effects on tax revenues.
Balancing Efficiency and Compliance:
- Physical verification strikes a balance between streamlining the registration process and ensuring compliance.
- It acts as a safety net to maintain the integrity of the GST system without unduly burdening genuine businesses.
Conclusion
The integration of Aadhar-based authentication and physical verification under GST into the GST registration process is a significant step towards streamlining taxation procedures in India. It offers efficiency, reduces duplication, and promotes ease of compliance. However, it is essential to strike a balance between efficiency and compliance, which is why physical verification remains a critical component of the GST ecosystem.
Aadhaar authentication and physical verification are complementary mechanisms that, when used judiciously, contribute to a robust and effective GST system. By leveraging technology and ensuring compliance, India’s GST regime continues to evolve, making taxation more accessible and transparent for businesses and taxpayers alike.





