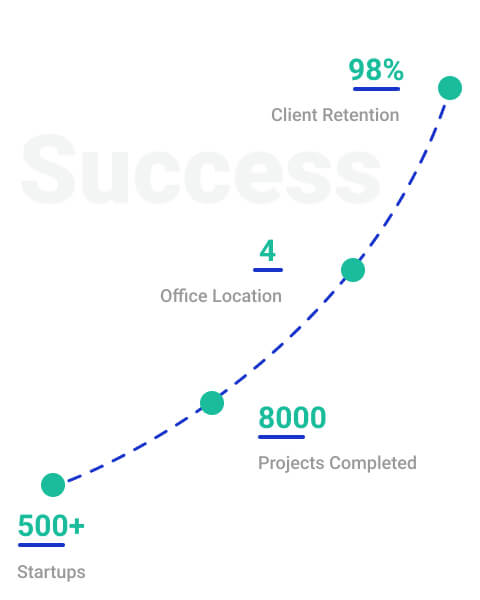
For startups a financial modelling is a finance tool where numeric representation of the startup's strategy along with vision is done. It forecasts company revenues, clients, KPIs, expenses, employee headcount and cash position.
Much more sophisticated companies will treat the financial model as being a budget and each division of the organisation will know its anticipated hiring, major cost and financial objectives. For early stage businesses, the financial model is a company plan which describes near-term expenses and objectives for the company, and then longer term shows the startup's development potential. Companies raising venture capital funding will use the projections to communicate with the VCs and will usually be a component of finance due diligence.
Understanding Financial Model of a Startup
A startup financial model is a strategic tool which enables businesses in order to anticipate their financial performance to help them make educated choices and to inform potential investors and stakeholders. It includes different components, including:
Purpose
The financial model represents a roadmap for the startup indicating its financial course based on historical data, assumptions and projections. It helps you to know the revenue generation, expense management, and profitability within a time period of generally one to five years.
Components
Creating an extensive financial model for startups requires several main elements which reveal the business's performance in the marketplace. The key components are:
|
Financial Statement
|
Description
|
Importance
|
|
Income Statement
|
Shows total revenue, expenses, and profits for a particular period.
|
Allows assessment of profitability and finding cost-saving opportunities based on revenue sources and expenses including salaries, rent, and marketing expenses.
|
|
Balance Sheet
|
Displays a picture of a company's financial situation at a certain time with its assets, liabilities, and equity.
|
Measures the firm's financial health and ability to meet up with its financial obligations as a function of assets versus equity and debts.
|
|
Cash Flow Statement
|
Shows just how cash moves in and from a company over a period of time, distinguishing money flows and outflows from working, financing, and investing activities.
|
Provides information into a company's liquidity, financial flexibility, and ability to produce cash flow to serve recurring costs and debts.
|
|
Debt Schedule
|
Provides a clear picture of any company's debt obligations like loan terms, repayment schedules, interest rates, along with outstanding balances.
|
Evaluates the company's general debt load, its ability to service debt, and also its projected potential debt repayment obligations.
|
Importance
A sample financial model for startups supports decision-making, raising money and strategic planning. They offer a framework for assessing business performance, determining risks and striving for sustainable development.
To include these parts in an entire financial model helps startups communicate their financial strategy, attract investors and make educated choices regarding business operations.
Benefits of Building a Financial Model For a Startup
Financial modelling for startups has many advantages for businesses:
1. Quantifiable Data for Fundraising
Financial models provide the quantitative information required for fundraising. At times investors want to see the company's financial projections in detail prior to they commit capital. A solid financial model could easily attract investors by demonstrating that the company can expand and profit.
2. Attraction & Evaluation of Investors
Investors assess potential returns and the viability of an opportunity to invest using the financial model of a startup. A financial model evaluates the company's financial well being, future prospects and risk factors. Supplying a clear financial picture helps businesses attract investors and raise funding.
3. Assessing Idea Sustainability
Financial models offer evidence of sustainability of an idea or strategy for a business. Analysing revenue projections, expense forecasts and cash flow dynamics helps businesses decide whether their ideas can realise sustainable returns. This informs decision making and refines business strategies for future success.
4. Understanding Cash Flow & Revenue
Financial models depict a detailed image of a business cash flow and revenue streams. Forecasting income and expenses over time reveals possible cash flow challenges, resource allocation and revenue generation strategies for the business. This enables better financial stability and financial management and development of the company.
Altogether, financial modelling for startups is needed for businesses to draw in investors, assess the viability of the ideas, and also understand their cash flow and earnings dynamics.
Key Elements of Financial Modelling for Startups
Financial modelling for startups involves considering different factors to make precise projections and sound decision making. The key components are given below:
|
Aspect
|
Description
|
Importance
|
|
Human Resources
|
New recruitment costs and salaries of existing workers included.
|
Workforce requirements are needed for accurate financial modelling for startups because labour costs impact the startup's expenses.
|
|
Revenue Assumptions
|
Projected income a startup seeks to produce.
|
Realistic revenue assumptions are crucial to drive accurate financial projections and analysing the business growth potential.
|
|
Balance Sheet
|
Displays startup assets & liabilities and also gives a quick picture of its financial situation at the conclusion of a reporting period.
|
Helps stakeholders understand the startup financial health & solvency to make much better decisions & strategic planning.
|
|
Income Statement
|
Integral to economic modelling, it calculates EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Amortisation, and Depreciation).
|
Gains visibility on startup profits and operational efficiency and guides resource allocation and overall performance evaluation.
|
|
Cash Flow Statement
|
Shows just how cash moves in and out of the startup.
|
Helps stakeholders understand cash flow dynamics to ensure liquidity for operations and investment activities.
|
|
Capital Expenditure
|
Costs to purchase physical assets like software, office space, and machinery.
|
Understanding capital expenditure is vital for budgeting & expense planning, allocation of resources, and portfolio management.
|
|
Sensitivity Analysis
|
Determines how changes in operating conditions or assumptions impact financial values.
|
Helps analysts evaluate the startup sensitivity to different factors and determine risks and opportunities for mitigation and optimization.
|
How to Create a Financial Model For Your Startup
Given below are some factors for financial modelling for startups:
Find the Financial Model's Objective
Before you jump into the creation process, define your financial model goal. Customise the complexity to your purpose - whether that is market sizing, fundraising or detailed cash flow analysis for an operational business.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify and group the company - relevant KPIs. These numerical factors ought to be measurable and trackable and constitute key benchmarks for monitoring performance and decision making.
Download a Financial Model Template for Startup
Use existing startup financial model templates to simplify things. Keep away from starting from scratch: it is inefficient and tedious. Many free startup financial model templates are available online to help build your financial model from. Choose StartupFino to get your simple startup financial model template and to help in your marketplace startup financial model.
Integrate Actual Results
Integrate your real financial data to the sample financial model for startups. For existing businesses, combining actual results with projections offers a realistic starting point and also helps determine discrepancies between expectation and reality.
Forecast Revenue
Start projecting revenue by analysing key drivers like customer base, sales effort and marketing expenditures. Consider revenue growth along with associated costs to understand income generation.
Project Headcount Requirements
Calculate the workforce required to attain your business objectives, including future growth and recruitment costs. Headcount is usually a big percent of startup costs and should be planned accordingly.
Estimate Other Expenses
Seek out startup financial model examples for expense scaling and anticipate extra costs as your business expands. Consider many expenditure categories and produce a balanced projection based on realistic financial scenarios.
Model Working Capital
Analyse payment cycles with clients and vendors to understand how working capital impacts your cash position. Plan for cash inflows and outflows to preserve liquidity needs for operations.
Review Projections
Review your financial projections carefully. Verify that the model matches your imagined thought and run a check to verify outcomes and assumptions.
You can then do strong financial modelling for startups which suits your business requirements and supports informed strategic and decision-making planning.
Building a Comprehensive Financial Modelling for Startups
A good financial model for your startup requires more than optimistic revenue projections. It demands a clear approach that touches all of your business finances. Actionable tips to create a good model are:
1. Get started with Revenue Projections
|
Step
|
Description
|
|
Understand your market
|
Conduct market research, competitor analysis, and industry reports on your target market size and prospective customers.
|
|
Define revenue streams
|
List all potential income sources (subscription fees, revenue, advertising revenue, licensing).
|
|
Pricing strategy
|
Define pricing based on manufacturing costs, competitor pricing, and perception of customer value.
|
|
Sales forecasts
|
Sales volume estimations based on market understanding, pricing approach, and growth assumptions.
|
|
Growth recommended assumptions
|
Make reasonable assumptions about revenue growth based on market trends and company strategy and frequently update projections with real-world information.
|
2. Estimate the Costs & Expenses
|
Category
|
Description
|
|
Costs of Sales
|
Direct costs for production/service delivery and customer acquisition costs.
|
|
Marketing & Sales
|
Budgets for advertising, promotions, sales team salaries, and other marketing expenses.
|
|
Research & Development
|
Expenses for product/software development, patent filings, and innovation.
|
|
General & Administrative
|
Overhead costs including executive salaries, legal fees, accounting, and insurance.
|
|
Depreciation & Amortisation
|
Depreciation of long-term assets and amortisation of intangible assets.
|
|
Interest and Taxes
|
Interest payments on loans and other tax responsibilities.
|
|
Unexpected Costs
|
Contingency fund for operational bumps and unexpected expenses.
|
3. Factor in Funding/Capital
Look at self-funding, venture capital, angel investors, bank loans or crowdfunding to help finance your startup.
4. Get ready for Contingencies
Keep an emergency fund, do scenario analysis regularly, buy insurance, build adaptability in your business model and create multiple future revenue streams to protect from risks and uncertainties.
Popular Types of Financial Models
Financial modelling for startups is important in analysing and forecasting a business's economic results. Some popular types of financial models across industries are given below
|
Model
|
Description
|
|
Three Statement Model
|
Links balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow for financial health assessment.
|
|
Budget Model
|
Plans annual budget based on income statement, aiding spending forecasts.
|
|
Forecasting Model
|
Predicts future costs for informed financial decisions, like production expenses.
|
|
Merger Model
|
Evaluates impact of mergers on combined entity's worth and capability.
|
|
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
|
Determines present value by adjusting future cash flows for investment assessment.
|
|
Sum of the Parts (SOTP) Model
|
Assesses net worth of individual business units within a conglomerate.
|
|
IPO Model
|
Estimates company's value before going public, indicating investor interest.
|
|
Leveraged Buyout Model
|
Analyses acquisitions financed with debt, assessing debt-cash flow relationship for investment purposes.
|
1. Three Statement Model
The basic kind of financial modelling for startups which links the balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement. It underlies other financial models and also gives a general picture of a company's economic health.
2. Budget Model
Used to plan a business annual budget and for economic analysis. This particular model relies on the income statement as a basis for the budget allocation and spending forecasting.
3. Forecasting Model
Predicts future costs in a company's budget based on planning and economic analysis. It helps businesses estimate future expenses (like production costs) and make financial decisions.
4. Merger Model
Offers insights on pro forma accretion of a startup during mergers or even acquisitions. This model helps stakeholders understand how a merger impacts the aggregate capability and worth of a combined entity.
5. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
Determines the present net value of a startup by adjusting future cash flows to the time value of money. DCF financial modelling for startups lets investors evaluate the company's total equity and investment potential.
5. Sum of the Parts (SOTP) Model
Assesses the net worth of individual units within an enterprise (often utilised by conglomerates which have several business units in various industries).
6. IPO Model
Determines the worth of a company before it goes public by estimating the valuation of its stocks in case they had been offered on the market. This model reveals investor interest and possible IPO pricing.
7. Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model
Analyses acquisitions in which the purchase is financed with considerable debt. It evaluates the connection between a business's debt and cash flow using cash flow reports, liabilities and revenue.
Key Points for Creating a Financial Model for Startups
A good financial modelling for startups is a necessity for businesses making informed choices and forecasting their financial future. Important considerations are:
|
Step
|
Description
|
|
1.
|
Define the problem and goal.
|
| |
- Identify the purpose and objectives of the financial model.
|
| |
- Clearly define the issue or challenge the model addresses.
|
|
2.
|
Limit variables and metrics.
|
| |
- Keep the number low to avoid ambiguity.
|
| |
- Focus on essential factors influencing financial decisions.
|
|
3.
|
Prioritise structure and organisation.
|
| |
- Use a well-structured Excel sheet with clear sections.
|
| |
- Use colours to differentiate metrics and formulas.
|
|
4.
|
Simplify formulas and calculations.
|
| |
- Use plain formulas for easier understanding.
|
| |
- Break down complex formulas for clarity and accuracy.
|
|
5.
|
Review and validate carefully.
|
| |
- Check formulas for errors and accuracy.
|
| |
- Get peer reviews for additional insights.
|
Why Choose StartupFino For Financial Modelling for Startups?
StartupFino offers top of the industry expertise and custom solutions for financial modelling for startups. Focused on emerging business needs, StartupFino offers financial modelling services that help your startup’s growth and success. Our experienced professionals understand startup and business trends to provide accurate financial projections. With StartupFino, startups get customised financial models based on their particular challenges and opportunities to make informed choices and attract investors.